Evaluation of the Concentrations of Nitrate, Nitrite and Heavy Metals in Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) Irrigated along the Amba Stream Lafia, Nasarawa State
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62050/ljsir2024.v2n1.275Keywords:
Nitrate, nitrite, heavy metal, spinach, irrigated waterAbstract
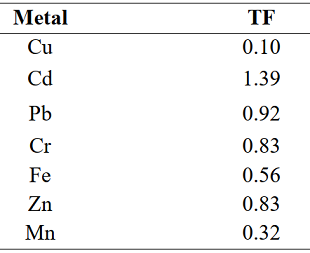
The concentrations of nitrate, nitrite and heavy metals were evaluated in the soil and edible portion of Spinach, irrigated along the Amba stream, Lafia, Nasarawa State. Nitrate, nitrite and heavy metals in the soil and spinach samples were determines using Spectrophotometric method. The mean concentrations (± Standard deviation) of nitrate ranged from 3042.91±1.62mgkg-1 to 4977.26±9.57mgkg-1, for Spinach while 5899.20±58.98mgkg-1 to stipulated by WHO and EC respectively. Mean of nitrite concentrations (NO2) (± standard deviation) ranged from 0.00029±0.00002mgkg-1 to 00102±0.00001mgkg-1 for all the spinach, while 0.00332±0.00002mgkg-1 to 0.00903±0.00002mgkg-1 for all soil were all below the mg/kg maximum specified by WHO. NO3 levels were generally higher than NO2.The mean concentrations of heavy metals ranged from Cd (1.29±0.01 mg/kg) to Fe (281.60±1.65 mgkg-1) for spinach while Cd (0.93±0.32 mgkg-1) to Fe (1084.1±1.73 mgkg-1) for soil. The values in spinach exceeded the permissible limit set by FAO. Transfer factors for the anions between the soil and spinach identify the efficiency of a spinach species to accumulate a given anion. There was positive correlation at p = 0.05 between the anions in the spinach. The transfer factors calculated were lower for all metals except cadmium (1.39).
Downloads
References
Ihekoronye, A.I and P.O. Ngoddy, 1985. Integrated Food Science and Technology for the Tropics, Macmillan Education Limited, Oxford, London, pp. 270-281.
Dich, J., Jarvinen, R., Knekt, P and PP.L. Penttila, 1996. Dietary intakes of nitrate, nitrite and NDMA in the Finnish mobile clinic health examination survey. Food Additives and Contaminants, 13:541-552. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652039609374439
Parkash, S., Tuli, G.D. and S.K. Basu, 1963. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. Part II, 10th Ed. Pp. 460-464.
Walker R., 1990. Nitrate and N-nitroso Compounds: A review of the occurrence in Food and Diet and the Toxicological implication. Food Additives and Contaminants, 7:717-768. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652039009373938
Santamaria, P, 2006. Nitrate in Vegetables: Toxicity Content, Intake and European Commission Regulation. Journal of Science and Food Agronomy, 86:10-17. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2351
Maynard, D.N., Barker, A., Minotti, A.V and N.H. peck, 1976. Nitrate accumulation in vegetables. Advances in Agronomy, 28: 71-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-2113(08)60553-2
Gangolli, S.D., Van Den Brandt, P. A., Feron, V., Janzowsky, J.C. Joeman, J.H., Spwijers, G. J.A., Spiegelhalder, B., Walker, R., and J.S. Wishnok, 1994. Assessment: nitrate, nitrite and N-niroso compounds. European Journal of pharmacology Envirmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 4(1): 1-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-6917(94)90022-1
FAO/WHO, 1995. Evaluation of certain food Additives and Contaminants. Geneva, World Health Organization, Joint FAO/WHO Expart Committee on Food Additives, World Heath Organization Technical Report Series, 859:29—35.
Aworth, O.c Hicks, J.R. Minotti, P.L and Lee,C.Y, 1980. Effects of plant age andnitrogen fertilization on nitrate accumulation and postharvest nitrite accumulation in fresh spinach. Journal of American Society for Horticultural Science, 105 (1): 18-20. https://doi.org/10.21273/jashs.105.1.18
Hunt, J., and M.K. Turner, 1994. A survey of nitrite concentrations in retail fresh vegetables, food Additives and Contaminants, 11(3): 327-332. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652039409374231
Raiswell, R.W., Brimblecombe, P., Dent, D.L. and P.S. Liss, 1980. Environmental Chemistry. Edward Arnold, Publishers Ltd., 18-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-7131-2790-4.50004-7
Radojevic, M. and N.V. Bashkin, 1999. Practical Environmental Analysis. Royal Society of Chemistry and Thoma Graham House, Cambridge, pp.180-430.
O’Dell B. and R.A Sunde, 1997. Handbook of Nutritionally Essential Mineral Elements. New York, NY Mercel Dekker, pp.33-41. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482273106
Corr’e W.J. and T. Brimer, 1999. Nitrate and nitrite in vegetables, Pudoc, Wageningen, P. 85.
Durner, J. and D.F. Klessing, 1999. Nitric oxide as a singal in plants. Current Opinoin on plant Biology, 2: 367-374. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(99)00007-2
Cantiffe, D.J, 1973b. nitrate accumulation in table beets and spinach as affected by nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium nutrition and light intensity. Agronomy Journal, 65: 563-565. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1973.00021962006500040012x
Santamaria, P., Elia A., Serio, F and E. Todaro, 1999. A Survey of nitrate and oxalate content in retail fresh vegetables. Jouranl of Science and Food Agriculture, 79: 1882-1888. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(199910)79:13<1882::AID-JSFA450>3.0.CO;2-D
Anjana, U.S., Iqbal, M. and Y.P.Abrol, 2006. Are Nitrate Concentrations in Leafy Vegetables within Safe Limits? Proceedings of the Workshop on Nitrogen in Enviromental, Industry and Agriculture. New Delhi, India, PP.81-84.
Zhou, Z.Y., Wang, M.J. and J.S. Wang, 200. Nitrate and Nitrite Contamination in Vegetables in China. Food rev. Int., 16: 61-76. https://doi.org/10.1081/fri-100100282
Lorenz, O.A, 1978. Potential nitrate levels in edible plant parts. In, Nitrogen in the environment, edited by Neilsen, D.R. and J.G. MacDonald; Academic Press, pp.201-2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-518402-1.50016-0
Stopes, C., Woodward, L., Forde, G. and H. Vogtman, 1988. The nitrate content of vegetable and salad crops offered to the consumer as fro, “organic” or “conventional” production systems. Biological Agriculture and Horticulture, 5 (3): 215-222. https://doi.org/10.1080/01448765.1988.9755146
Zink, F.W., and. M. Yamaguchi, 1962. Studies on the Growth rate and Nutrient Absorption of the Head Lettuce. Hilgradia, 32 (11): 471-500. https://doi.org/10.3733/hilg.v32n11p471
Aremu, M. O., Oko, O. J. & Andrew, C. (2017). Ground water and river quality assessment for some heavy metals and physicochemical parameters in Wukari town, Taraba State, Nigeria. Int. Journal of Sci., 6(5), 73–80. https://doi.org/10.18483/ijSci.1298
Awofolu, O., Mbolekwa, Z., Mtshemla, V. & Fatoki, O. (2005). Levels of trace metals in water and sediment from Tyume River and its effects on an irrigated farmland. Water SA, 31(1), 87-94. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v31i1.5124
Khariah, J., Zalita, M.K., Yin, H.Y. and Amina, A. (1984). The uptake of heavy metals by fruits, type vegetables in selected Agricultural Areas of Malaysia. Pakista Journal of Biological Science, 7(8), 37-42. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2004.1438.1442
Lastra O.C, (2003). Derivative Specttrophotometric Determination of Nitrate in Plant Tissue. Santiago: Universidad de Chile. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/86.6.1101
LaMotte, (2000). Smart Spectro Water and Waste water Procedure Analysis Manual. LaMotte incorporated, pp. 68 – 180.
WHO (2003).Nitrate and nitrite in drinking-water: Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water: Quality. World Health Organization. Retrieved May 21, 2014 from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/nitrate-nitrite-background-document.pdf
Matthew, N. B, Augustine, A. U, Shaibu, S, E, Akpomie, K. G & Etim, E. U (2019). Spectroscopic evaluation of nitrate and nitrite concentrations in selected fruits and vegetables. International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Science, 3(9), 32-35.
Swallow B. (2004). Nitrates and Nitrites Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment. Client Report FW0392.
Alexander P, Handawa P and Charles T.U (2016). Determination of Nitrate and Nitrite contents of some Edibles Vegetables in Guyuk Local Government Area of Adamawa State, Nigeria. American Chemical Science Journal, 13(3): 1 – 7. https://doi.org/10.9734/acsj/2016/23387
Speijers GJA and Van den Brandit P.A (2003). Nitrate (and potential endigenous formation of N- nitroso compounds). WHO Food Additives Series 50 (2003). Retrieved from: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/ v50je06.htm on May 24, 2017.
Uwah E.I.J Abah, N.P. Ndahi and V.O.Ogugbuaja, 2009. C0ncentration Levels of Nitrate and Nitrite in soils and some Leafy Vegetables Obtained in Maiduguri, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Science in Environment Sanitation, 4(3):233-244.
Lokeshwari, H. and G.T. Chandrappa, 2006. Impact of heavy metal contamination of Bellandur Lake on soil and cultivated vegetation. Current Science, 91(5): 622-627.
European Food Safety Authority EFSA (2008). Nitrate vegetables-Scientific opinion of the penal on contaminants in the food chain. European Food Safety Authority Journal, 689:1 – 79.
Uwah EJ, Ndahi NP, Abdulrahman FI, Ogugbuaja VO (2011). Heavy Metal Levels in Spinach (Amaranthus caudatus) and Lettuce ( Lactuca sativa) Grown in Maiduguri, Nigeria. Journal Environmental Chemistry. Ecotoxicol. 3(10):71-78.
Abulude OF (2005). Trace Heavy Metals contamination of Soils and Vegetation in the vicinity of livestock in Nigeria. EJEAF Che., 4(2): 863 – 870.
Harrison, R,M, and M. B. Chirgawi, 1989. The assessment of air and soil as contributors of some trace metals in vegetable plants I. Use of a filtered air growth cabinet. Science of Total Environment, 83: 13─ 34.
Anjana, Umar, S., Iqbal, M. and Abrol, Y. P. (2009). Are nitrate concentrations in leafy vegetables within safe limits? Current Science 92 (3): 355 – 360.
Akan, J. C., Abdulrahma, F. I., Ogugbuaja, V. O. & Ayodele, J. T. (2009). Heavy metals and anion levels in some samples of vegetable grown within the vicinity of Challawa Industrial Area, Kano State, Nigeria. American Journal of Applied Sciences, 6(3), 534–542. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajas.2009.534.542
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Lafia Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









