Anti-diabetic Effect of Ethanol Leaf Extract of Ziziphusspina-christi on Alloxan Induced Albino Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62050/ljsir2024.v2n1.262Keywords:
Phytochemicals , Ziziphus Spina Christi, Marker, AntioxidantAbstract
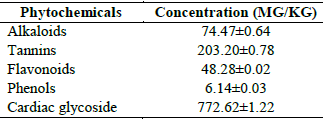
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of an ethanol extract obtained from the leaves of Ziziphus spina christi on alloxan-induced diabetic rats using standard analytical procedures. Fifteen Albino Wistar rats were divided into five groups, each consisting of three rats. The groups included a normal uninduced rats as control group, a diabetic untreated group as the diabetic control, a group treated with a dosage of 150mg/kg body weight, a diabetic group treated with metformin as the standard drug, and another treatment group. The levels of liver marker enzymes, such as alanine transaminase (60.7±3.25) and aspartate transaminase (69.5±1.84), as well as liver function parameters like total protein (7.47±0.02), were found to be higher in the diabetic control group compared to the normal control and other treatment groups. However, in all the treatment groups, there was a significant decrease observed in alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and alkaline phosphatase. The level of kidney function markers such as blood creatinine (1.58±0.07) and blood urea (43.50±0.86) were significantly (p˃0.05) higher in the diabetic control group when compared to the normal control. However, significant (p˃0.05) reductions in blood creatinine and blood urea were observed in all the treatment groups. The presence of phytochemicals such as alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, phenols, and cardiac glycosides in the ethanolic extract of sidr leaves were probably responsible for the anti-diabetic activities of the plant extract. In conclusion, the antidiabetic effect of ethanolic extract of sidr as observed in this study may be attributed to its antioxidant properties.
Downloads
References
American Diabetes Association. (2007). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care, 30(Suppl. 1), S42-S47. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-S042
World Health Organization. (2016). Diabetes facts. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.10929
Magliano, D. J., Shaw, J. E., Shortreed, S. M., Nusselder, W. J., Liew, D. and Barr, E. L. (2008). Lifetime risk and projected population prevalence of diabetes. Diabetologia, 51(12), 2179-2186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-008-1150-5
Al-Ghamdi, A. A. M., El-Zohri, M. and Shahat, A. A. (2019). Hepatoprotective, nephroprotective. American Chemical Society, 89(18), 4808-4809. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00421
Michel, C. (2011). Anti-diabetic activity and stability study of the formulated leaf extract of Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) Willd with the influence of seasonal variation. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 133, 53-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.09.040
Ogbera, A. O., Adedokun, A., Fasanmade, O. A., Ohwovoriole, A. E. and Ajani, M. (2005). The foot at risk in Nigerians with diabetes mellitus: The Nigerian scenario. International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 4, 165–173. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.4.165
Gupta, P. D. and De, A. (2012). Diabetes Mellitus and its herbal treatment. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences, 3(2), 6-21. https://doi.org/10.7897/2230-8407.03226
Mamun-or-Rashid, A., Hossain, M. S., Nain, Hassan B., Kumar Dash, M., Sapon, A. and Sen, M. K. A. (2014). Review on medicinal plants with antidiabetic activity. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 3(4), 149-159. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.3(4).149-59
Chen, Z., Duan, H., Wang, M., Han, L., Liu, Y. and Yang, S. (2015). Synthesis cytotoxicity and haemolytic activity of Pulsatilla saponin a D derivatives. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 25, 2550-2554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.04.050
Apulu, N., Dada, J. O., Odama, L. E. and Galadima, M. (1994). Antibacterial aqueous extracts of some Nigeria Medicinal Plants. Nigerian Journal of Botany, 7, 45-48. https://doi.org/10.2307/41220815
Mahomoodally, M. F. (2013). Traditional medicines in Africa: An appraisal of ten potent African medicinal plants. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.003
Schmelzer, G. H. and Fakim, A. G. (2013). Medicinal plants 2. Prota 2008, 11, 2-6. https://doi.org/10.3763/eprota
Pawlowska A. M., Camangi, F., Bader, A. and Braca, A. (2009). Flavonoids of Zizyphus jujuba L. and Zizyphus spina-christi (L.) Willd (Rhamnaceae) fruits. Food Chemistry, 112(4), 858-862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.023
Zhang, and Sui, D. (2017). Metformin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in a rat model of low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Experi. and Therapeutic Medicine, 14, 383-390. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4533
Ewenighi, C., Dimkpa, U., Onyeanusi, J., Onoh, L., Onoh, G. and Ezeugwu, O. (2015). Estimation of glucose level and body weight in alloxan-induced diabetic treated with aqueous extract of Garcinia Kola seed. Ulutas Medical Journal, 1, 26-30. https://doi.org/10.5455/umj.20150403013730
Lin, E. H. B., Rutter, C. M., Katon, W., Heckbert, S. R., Ciechanowski, P., Oliver, M. M., ... and Williams, L. H. (2010). Depression and advanced complications of diabetes: A prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care, 33(2), 264-269. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1068
Lee, A. and Morley, J. E. (1998). Metformin decreases food consumption and induces weight loss in subjects with obesity with type II non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Obesity Research, 6, 47-53. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1550-8528.1998.tb00362.x
Abalaka, M. E., Daniyan, S. Y. and Mann, A. (2010). Evaluation of the antimicrobial activities of two Ziziphus species (Ziziphus manuritiana L. and Ziziphus spina christi L) on some microbial pathogens. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 4, 135-139. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPP09.354
Yossef, H., Khedr, A. A. and Mahran, M. Z. (2011). Hepatoprotective activity and antioxidant effects of EL Nabka (Zizyphus spina-christ) fruits on rats hepatotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride. Natural Science, 9(2), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.4236/ns.2011.92002
Ghafoor, A. O., Qadir, H. K. and Fakhri, N. A. (2012). Analysis of phenolic compounds in extracts of Ziziphus spina-christi using RPHPLC method. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 3158-3163. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPP09.354
Lenzen, S., Tiedge, M., Jorns, A. and Munday, R. (1996). Alloxan diabetes: Mechanism of action of alloxan and streptozotocin on beta cells of the rat pancreas. Physiological Research, 50, 537-546. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.932211
Szkudelski, T. (2001). The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in pancreatic beta cells of the rat. Physiological Research, 50, 537-546. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.932211
Davidson, M. B., & Peters, A. L. (1997). An overview of metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Medicine, 102, 99-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9343(96)00430-2
Chakraborty, S. B. and Hancz, C. (2011). Application of phytochemicals as chic and anti-stress agents in finfish culture. Reviews in Aquaculture, 3, 103-119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-5131.2011.01020.x
Niamat, R., Khan, M. A., Khan, K. Y., Ahmed, M., Mazari, P., Ali, B., ... and Zafar, M. (2012). A review of Zizyphus spinachristi. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical. https://doi.org/10.21065/19204159.3.1.8
Zhang, C. and Pang, S. (2019). A possible mechanism in improving insulin resistance in diabetic rat models. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2019, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1352031
Melmed, S., Polonsky, K. S., Larsen, P. R. and Kronenberg, H. M. (2016). Williams Textbook of
Endocrinology (13th ed.). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2013-0-14012-1
Depression and Advanced Complications of Diabetes: A prospective cohort study. (2010). Diabetes Care, 33(2), 264-269. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1068
Othman, A. I., Amer, M. A., Abdet-ogb, and Samaha, R. (2009). Effects of the methanolic extracts of Zizyphusspinachristi, Oleaeuropaca, and Morusalba leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The Egyptian Journal, 771.
Navarro, C. M., Montilla, P. M., Martin, A., Jimenez, J., and Utrilla, P. M. (1993). Free radicals scavenger and antithepatotoxic activity of Rosmarinus. Planta Medica, 59, 312-314. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-959707
Almadal, T. P. and Vilstrup, H. (1988). Strict insulin treatment normalizes the organic nitrogen contents and the capacity of urea-N synthesis in experimental diabetes in rats. Diabetologica, 31, 114-118. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00274764
Guyton, A. C. and Hall, J. E. (2000). Insulin, glucagon and diabetes mellitus. In Textbook of Medical Physiology (10th ed., pp. 84-897). WB Saunders. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.cp010209
Okasha, S. A., Takadom, F. M. K. and Hassan, M. K. (2017). Combination effect of Zizyphus spina-christi and hyperthermia on liver and kidney affected by EAC in mice. International Advanced Research, 3, 1486-1493. https://doi.org/10.30574/iar-2017-11-3-45
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Lafia Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









