MANUFACTURING SOAP FROM WASTE COOKING OIL USING COLD AND HOT PROCESSES
Mots-clés :
Soap, oil, saponification, pH, moisture contentRésumé
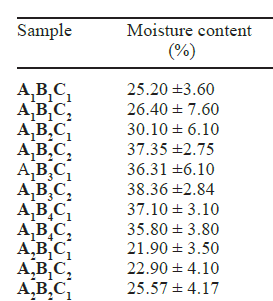
The conversion of waste cooking oil to soaps using endothermic (hot) and exothermic (cold) soap making processes was investigated. Waste cooking oils were collected locally and characterized using standard methods and found to have acceptable saponification value (258.9 g).Various soaps were prepared by factorial combinations (A, B, C)using the following parameters: amount of NaOH, oil content and molding time. The soaps prepared gave a pH range of 9.85± 0.45 to11.20±0.30 and 10.65±0.65 to 12.20± 0.10 for the cold and
hot processes respectively. The % moisture contents of the soap made using cold process were between the ranges of 25.20± 3.60% to 38.36± 2.84% while the soaps made from hot process had a % moisture content of 21.90± 3.50% to35.74± 3.54%. Total fatty matter (TFM) content of the cold process soaps gave values of 10.60% - 60.00% while the hot process soaps reported values ranging from 30.00% - 71.00%.
##plugins.themes.default.displayStats.downloads##