PHYSICO-CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF EARLY AND LATE HARVESTED IMPROVED AND LOCAL SWEET POTATO (Ipomoea batatas (L) Lam) CULTIVARS ON THE JOS PLATEAU
Keywords:
Cultivars, Proximate analysis, Early harvest, Late harvest, Calorific valuesAbstract
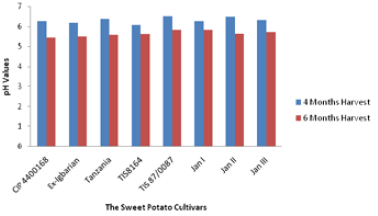
The physicochemical composition and the energy values of the flours of both identified improved sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L) Lam) cultivars: CIP4400168, Ex-Igbariam, Tanzania, TIS 8164 and TIS 87/0087 and three local varieties (Land-races) of sweet potato were investigated. The cultivars were harvested after 4 months (early harvest) and 6 months (late harvest) to determine their suitability for the formulation of sweet potato secondary products. The root of each harvestwas weighed, washed, scrubbed, chipped to 1 x 1 x 6mm
dimension, dried, milled into powder, sieved through 250μm mesh size sieve to obtain sweet potato flour. The flour was proximately analysed for moisture content (MC), Protein, Lipid, Fibre, Ash, Starch, Calorific value and pH using standard methods.The late harvest differed significantly in the parameters examined. The flour had low percentage moisture content ranging between 5 and 7.04% for late and early harvests respectively, indicative of long shelf life characteristics and low chances of attack by microorganisms. The crude protein values were higher (7.04%) in the flours of the early harvest but low (0.77%) for late harvest. The lipid concentration of the cultivars was low, 0.24 and 1.67% for the flours of 4 and 6 months harvests respectively. The fibre mean values of the flours were high (3.80%) in the 6 months harvest but low (1.24%) in the 4 months harvest.The ash content of the samples ranged between 0.83 and 2.56% for the flours of 6 and 4 months harvest respectively. The mean percentage values for starch of the flours were high ranging between 79.43 and 89.76% for 4 and 6 months harvested cultivars.
Downloads