PRELIMINARY TOXICITY EVALUATION OF SOIL CONTAMINATED WITH PETROLEUM DERIVATIVES ON SOME CROP PLANTS
Keywords:
Petroleum derivatives, Sorghum bicolor, Toxicity, Zea maysAbstract
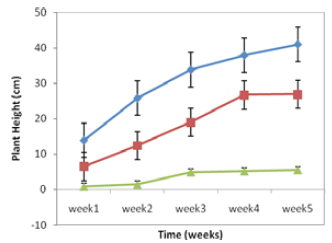
The germination and growth of Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor were investigated on soils contaminated with different petroleum derivatives. This was carried out with a view to ascertaining the toxicity effects of these derivatives on the crop plants. Soil was collected from area with no previous contamination and was filled inside polythene bags. The experimental setup for each contaminant was a complete randomized design with three replicates. Each of the petroleum derivatives which include diesel oil (AGO), spent engine oil and lubricant oil each had three treatments i.e. 0 ml, 50 ml and 100 ml. The 0 ml treatment represents control where the soil was mixed with distilled water only. Five seeds of each crop plant were picked at random and sown on the soils containing the treatments and the experiments were monitored for five weeks. The germination percentage was calculated daily for seven days while the plant height and leaf areas were determined weekly. Results showed that the controls of all the crop plants had the highest percentage germination while the treatment that had 100 ml contaminations had the lowest. It was also observed, the higher the diesel oil contamination, the lower the leaf areas of Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor
Downloads