SOIL PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND MICROFLORA AS INFLUENCED BY PARAQUAT APPLICATIONS
Keywords:
Paraquat, Soil, Bacteria, Fungi, Physicochemical propertiesAbstract
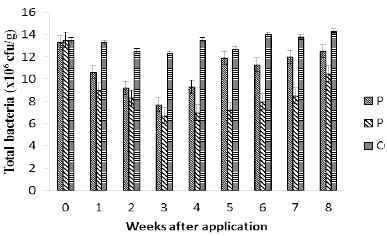
A field experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of paraquat (1, 1’-di methyl-4,4’-biyridinium dichloride) at the recommended and twice the recommended field application rates on soil physicochemical properties and microorganisms. The effects of the herbicide on soil pH, organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus content and cation exchange capacity were analyzed along with microbial populations and the growth and distribution of representative soil microorganisms were obtained using standard procedures. There was no significant effect of paraquat on soil physicochemical properties at P>0.05. Paraquat applications at both concentrations caused reduction in the bacterial and fungal populations with twice the recommended rate having more adverse effect when compared with the control while the fungal populations were more adversely affected than the bacteria populations by herbicide treatment. Reduced number of predominant bacteria and fungi genera as well as the elimination of some secondary genera as observed in paraquat treated soils could be detrimental to the sustainability of soil fertility. These results are discussed in line with the soil management practices for sustainable crop production
Downloads