GROUNDWATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT AROUND IGBATORO DUMP YARD USING GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGY
Keywords:
Geospatial Information Technology, Water Quality Index, Pollution, TreatmentAbstract
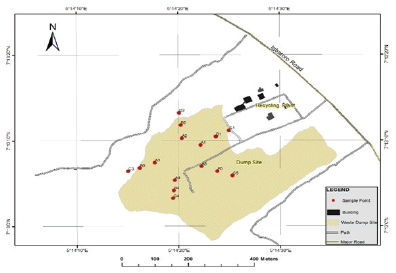
This study evaluated the degree of groundwater pollution near the dump yard at Igbatoro, Ondo State. The entire study area was digitized and georeferenced in order to produce pollution maps from results obtained. Forty-five (45) water samples were obtained from fifteen (15) different locations at distances ranging from 50 m to 150 m around the refuge dump. The coordinate of the sample collection points were acquired using handheld GPS. Samples recovered were taken to the laboratory in an air tight plastic container where the physcio-chemical characteristics and other parameters needed for the computation of Water Quality Index (WQI) was calculated. Some parameters evaluated includes but not limited to the followings: dissolve oxygen (DO), total suspended solid (TSS), pH, total dissolved solid (TDS), turbidity, concentration of nitrate and nitrite, chloride, phosphate, total coliform count, and heavy metals including iron, lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc. Results obtained were compared with WHO standards for drinking water and was also used for calculating WQI for the study area. The result showed that WQI in the area ranged from 41.394 – 59.515 (50 m), 58.840 – 66.556 (100 m) and 71.111 – 85.384 (150 m). The water quality range from bad (50 m) to good (150 m) i.e. the quality of the water improved as the distance away from the dump yard increased. Other parameters investigated also had values higher than the permissible limits recommended by WHO.
Downloads