Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of Luffa (Luffa cylindrica) and Banana (Musa acuminata) Fibre Reinforced Recycled Low-Density Polyethylene (rLDPE)
DOI :
https://doi.org/10.62050/ljsir2025.v3n2.607Mots-clés :
Polyethylene, Luffa, Banana fibresRésumé
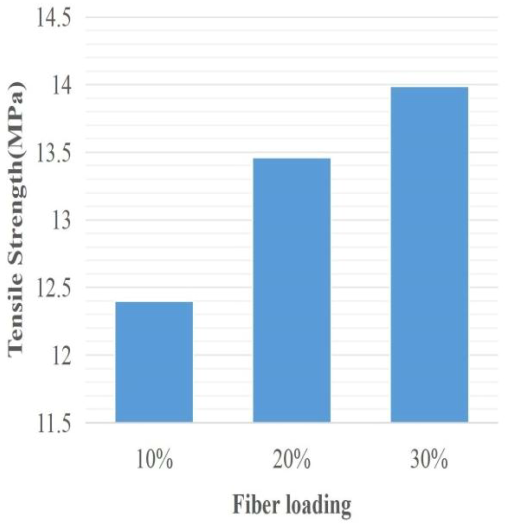
In response to the environmental concerns posed by low-density polyethylene (LDPE) pollution, this study explores the potential of natural fibers—specifically banana and luffa fibers—as reinforcements in recycled LDPE composites. Composites were fabricated by blending post-consumer rLDPE with banana and luffa fibers at weight ratios of 10%, 20%, and 30%. Mechanical properties: tensile strength, flexural strength, elongation at break, and impact resistance tests were evaluated. Results showed that banana fiber composites exhibited an increase in tensile strength from 12.4 MPa to 13.99 MPa with increasing fiber content (10%–30%), The flexural strength decreases from 125.9 MPa at, 105MPa, and 92.74 MPa at 30% of fibre loading, while elongation at break, the elongation increases from 14.51% at 10% to 35.31% at 30%. However, both flexural strength and impact resistance decreased with increased fiber loading, likely due to poor fiber-matrix interfacial bonding. Optimal performance for banana-reinforced composites was observed at 30% fiber content for tensile strength, and at 10% for flexural strength. In contrast, luffa fiber composites showed a decrease in tensile strength from 11.84 MPa to 10.07 MPa as fiber content increased, attributed to weak interfacial adhesion. Flexural strength increased from 10MPa to 57.78MPa fiber loading. Elongation decreased from 44.62%-25%, but slightly increased 25%-28% as fibre loading increases due to poor fiber-matrix interfacial bonding. Overall, banana fiber demonstrated more consistent and favorable mechanical performance than luffa, particularly in tensile properties, highlighting its potential as a sustainable reinforcement material in rLDPE composites to mitigate plastic waste and reduce environmental impact.
##plugins.themes.default.displayStats.downloads##
Références
Pickering, K. L., Efendy, M. G. A., & Le, T. M. (2016). A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 83, 98–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.038
Sanjay, M. R., Madhu, P., Jawaid, M., Senthamaraikannan, P., Senthil, S., & Pradeep, S. (2018). Characterization and properties of natural fiber polymer composites: A comprehensive review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 172, 566–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.101
Faruk, O., Bledzki, A. K., Fink, H. P., & Sain, M. (2012). Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Progress in Polymer Science, 37(11), 1552–1596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.04.003
Thakur, V. K., & Thakur, M. K. (2014). Processing and characterization of natural cellulose fibers/thermoset polymer composites. Carbohydrate Polymers, 109, 102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.03.039
Hao, A., Chen, H., & Chen, L. (2021). Advanced natural fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review on their processing, properties, and applications. Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, 6(3), 209–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2021.03.002
Azam, A., Khubab, M., & Ilyas, R. A. (2021). A review on the environmental and health impacts of biocomposite materials: Present and future trends. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 417, 126022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126022
Mohammed, L., Ansari, M. N. M., Pua, G., Jawaid, M., & Islam, M. S. (2015). A review on natural fiber reinforced polymer composite and its applications. International Journal of Polymer Science, 2015, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/243947
Peças, P., Carvalho, H., Salman, H., & Leite, M. (2018). Natural fibre composites and their applications: A review. Journal of Composites Science, 2(4), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2040066.
Wilczek, G. (2016). Polystyrene. In Brydson's Plastics Materials (8th ed., pp. 347–373). Butterworth-Heinemann. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-35824-8.00015-3
Etemadi, M., & Behrooz, R. (2020). Mechanical and thermal properties of wood flour/polystyrene composites. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 33(7), 903–918. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705718816827
Boumaza, L., Bezazi, A., & Garcia-del-pino, G. (2021). Effect of flax fiber reinforcement on the mechanical behavior of expanded polystyrene for building applications. Journal of Natural Fibers, 18(9), 1334–1347. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2019.1685376
Li, X., Tabil, L. G., & Panigrahi, S. (2007). Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: A review. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 15(1), 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-006-0042-3
Kabir, M. M., Wang, H., Lau, K. T., & Cardona, F. (2012). Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Composites Part B: Engineering, 43(7), 2883–2892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.04.053
Boynard, C. A., & D'Almeida, J. R. M. (2000). Morphological characterization and mechanical behaviour of vegetable sponge (Luffa cylindrica). Polímeros, 10(2), 70–74. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-14282000000200009
Ghani, M. A., & Salleh, Z. (2021). A review on the potential of Luffa cylindrica fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Journal of Natural Fibers, 18(12), 2051–2065. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2019.1708819
Oboh, I. O., Nworah, O. B., & Oseh, J. O. (2020). Mechanical and wear properties of Luffa cylindrica-reinforced polyester composite. Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 11(5), 762–771.
Asim, M., Jawaid, M., Abdan, K., & Ishak, M. R. (2016). The effect of hybridization on the mechanical and thermal properties of Luffa/jute fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. Fibers and Polymers, 17(4), 558–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-5991-6
Kumar, R., Ul-haq, M., Raina, A., & Anand, A. (2019). Mechanical and tribological performance of luffa-fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 41(2), 65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1549-0
Shen, J., Weng, J., Wang, S., & Li, X. (2018). Sound absorption and vibration damping properties of Luffa cylindrica fiber/epoxy composites. Journal of Porous Materials, 25(4), 1145–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0524-7
K-w, A. A., & Horváth, I. (2020). A review on the applicability of natural fiber-reinforced polymer composites in the automotive industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 256, 120412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120412
La Mantia, F. P., & Morreale, M. (2011). Green composites: A brief review. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 42(6), 579–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.01.017
Mohanty, A. K., Misra, M., & Drzal, L. T. (Eds.). (2005). Natural fibers, biopolymers, and biocomposites. CRC press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203508206
Yang, H. S., Kim, H. J., Son, J., Park, H. J., Lee, B. J., & Hwang, T. S. (2004). Rice-husk flour filled polypropylene composites; mechanical and thermal properties. Composite Structures, 63(3-4), 305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(03)00179-X
Chen, Y., Liu, Y., & Lv, Y. (2019). The effect of fiber content on the mechanical properties of sisal fiber-reinforced polylactic acid composites. Polymers, 11(5), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050893
Asim, M., Abdan, K., Jawaid, M., Nasir, M., Dashtizadeh, Z., Ishak, M. R., & Hoque, M. E. (2018). A review on pineapple leaf fibres and its composites. International Journal of Polymer Science, 2018, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9505676
Dhakal, H. N., Zhang, Z. Y., & Richardson, M. O. W. (2007). Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Composites Science and Technology, 67(7-8), 1674–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.06.019
Téléchargements
Publiée
Numéro
Rubrique
Licence
(c) Copyright Osuegba Osuendo Solomon, U. Adamu, S. Mamman, O. B. Aduke, S. Yusuf, D. P. Habila, B. M. Nathaniel, K. H. Uzeru (Author) 2025

Ce travail est disponible sous licence Creative Commons Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International.









