Comparative Study of Activated Kaolin From Ahoko Clay and Lemu Clay
DOI :
https://doi.org/10.62050/k9vxhw41Mots-clés :
Clay, Activated Kaolin, Kaolinite, Climate Change, Greenhouse GasRésumé
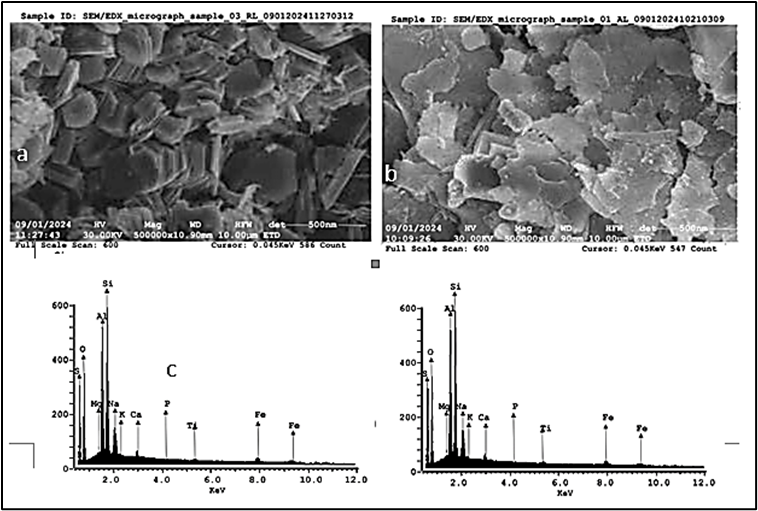
A major issue facing the globe today is climate change and global warming, which are caused by the use of fossil fuels in transportation and other industries that generate large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. These CO2 gases is the major greenhouse gas which causes damages to health and environment. In this work, Ahoko kaolin and Lemu kaolin were activated and compared as an adsorbent for CO2 adsorption from the atmosphere. Both clays were activated using acid in order to improve the adsorbent. The BET analysis was carried out to determine the surface area, pore volume and pore size of both samples before and after activation. The result shows that the kaolin from Ahoko has a larger surface area with 82% increment of the activated samples compared to the raw samples. Also the activated Lemu kaolin increases by 132% compared to raw Lemu kaolin. The SEM analysis was also done before and after the activation of both samples to identify and interpret the surface morphology of the adsorbent (Ahoko kaolin and Lemu Kaolin). The FT-IR revealed that both samples have characteristic peaks associated with hydroxyl group, silicate group and oxides group. The research shows that the activated kaolin shows a better result compared to the raw kaolin from both samples. It also shows that activated kaolin from Lemu will likely capture CO2 more, compared to activated kaolin from Ahoko.
##plugins.themes.default.displayStats.downloads##