Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Porcine Salmonella in Nasarawa state, North Central Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62050/faic2025.bop25.002Keywords:
Antibiotic Resistance, Porcine Salmonella, Nasarawa StateAbstract
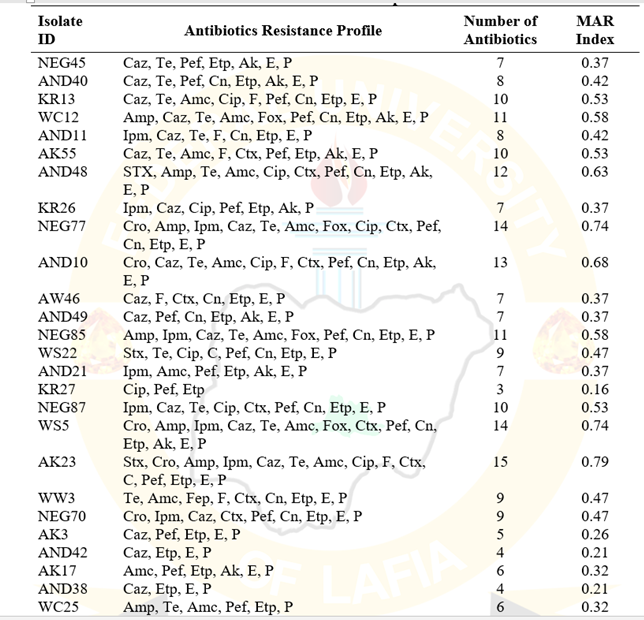
Salmonellosis is among the important zoonosis attracting global attention recently. The burden of this pathogen is rising due to antibiotics resistance threatening food safety, therapeutic outcomes and manpower productivity mostly in developing nations. The aim of this study was to determine the Antibiotic resistance profile of Porcine Salmonella in Nasarawa State, Nigeria. A total of 637 freshly voided fecal samples were collected and subjected to culture and isolation according to methods described by Office International des epizooties (OIE). Antibiotic susceptibility patterns of the isolates were determined against mostly used antibiotics in veterinary and human medicine. The Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed that all the isolates were resistant to Erterpenem (100%),some highly resistant to Penicillin G (96.7%) and Erythromycin (90.0%) but susceptible to Cefepime (96.7%), Sulphamethoxazole (83.3%), Chloramphenicol (80.0%), Ceftriaxone (76.7%), Ampicillin (60.0%), Cefoxitin (73.3%), Imipenem (53.3%), Nitrofurantoin (43.3%), Cefotaxime (33.3%), Ciprofloxacin (30.0%), Pefloxacin, Amikacin and Gentamicin (23.3%), Tetracycline and Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid (13.3%) while susceptibility for Erythromycin and Penicillin G was 3.3%. Intermediate resistance ranged from 43.3% for Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid, 36.7% for Amikacin, 33.3% for Ciprofloxacin, 30% for Nitrofurantoin, 26.7% for Cefotaxime and Tetracycline, 20.0% for Ceftazidime and Gentamicin,16.7% for Ampicillin and Imipenem, 10.0% for Chloramphenicol and Cefoxitin while Sulphamethoxazole/Trimethoprim, Ceftriaxone and Erythromycin had 6.7%. The MAR index ranged from 0.21 to 0.97 indicating high levels of environmental contamination with antimicrobials. This study confirms pigs as reservoirs of resistant Salmonella highlighting the need for One-Health approach to safeguard the health of the populace.
Downloads